Implementing Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity has become an essential aspect of every organization’s operations. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and traditional security measures are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data and critical systems. As a result, many organizations are turning to zero trust architecture to enhance their security posture. In this article, we will explore what zero trust architecture is, the benefits, how to implement it, and much more.
What is “Zero Trust Architecture” or ZTA?
Zero trust architecture is a security model that assumes that every user, device, and network component is a potential threat. As a result, it requires strict authentication and authorization measures to limit access to sensitive data and critical systems. In a zero trust environment, users and devices must be verified before they are granted access to any resource. This is done by implementing continuous authentication and authorization checks throughout the entire network.
Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing zero trust has several benefits, including:
Improved Security
Zero trust architecture provides a more secure environment by limiting access to sensitive data and critical systems. It assumes that every user and device is a potential threat and requires strict authentication and authorization measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Reduced Risk
By limiting access to sensitive data and critical systems, zero trust architecture reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. It also helps organizations comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Increased Agility
Zero trust architecture allows organizations to be more agile by enabling them to adopt new technologies and applications without compromising security. It provides a flexible and scalable security framework that can adapt to changing business needs.
Enhanced Visibility
Zero trust architecture provides enhanced visibility into network activity, allowing organizations to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time.
Barriers to the Zero Trust Security Model
There are several barriers to the zero trust model that organizations may face when implementing this security framework. Some of the common barriers include:
- Legacy systems: Legacy systems that do not support modern authentication and authorization protocols can be a significant barrier to implementing zero trust. These systems may need to be upgraded or replaced, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Cost: Implementing zero trust architecture can be expensive, especially for large organizations with complex networks. The cost of purchasing and implementing new security solutions, as well as ongoing maintenance and monitoring, can be a significant barrier for some organizations.
- User Experience: Implementing zero trust may require users to complete additional authentication steps and may limit their access to resources. This can result in a negative user experience, which can affect productivity and increase frustration.
- Lack of expertise: Implementing zero trust architecture requires expertise in network security, authentication, and authorization. Some organizations may not have the necessary expertise in-house and may need to outsource the implementation to a third-party provider.
- Resistance to change: Implementing zero trust architecture requires significant changes to the organization’s security policies and procedures. Some employees may resist these changes, which can make implementation challenging. Overcoming these barriers requires a comprehensive approach that includes careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing monitoring and maintenance. With the right resources and approach, organizations can successfully implement zero trust architecture and enhance their security posture.
How to Implement Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing zero trust architecture requires a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of the network. Here are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Define the Scope
The first step in implementing zero trust architecture is to define the scope of the project. This involves identifying all the applications, data, and systems that require protection. It also involves identifying all the users and devices that need access to these resources.
Step 2: Develop a Security Policy
Once the scope has been defined, the next step is to develop a security policy. This policy should outline the rules and procedures for access control, authentication, and authorization. It should also define the roles and responsibilities of users and administrators.
Step 3: Implement Access Control
Access control is a critical component of zero trust architecture. It involves implementing strict authentication and authorization measures to limit access to sensitive data and critical systems. This can be done by implementing multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and continuous monitoring of user activity.
Step 4: Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing the network into smaller, more secure segments. This helps to limit the spread of malware and other threats. It also allows organizations to control access to specific resources based on user roles and responsibilities.
Step 5: Monitor and Analyze Network Activity
Continuous monitoring and analysis of network activity is essential in a zero trust environment. This helps organizations detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. It also allows them to identify and address security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
We suggest using either Microsoft or AWS to support your ZTA model to build secure and scalable architectures.
FAQs
What is the difference between traditional security measures and zero trust architecture?
Traditional security measures assume that everything inside the network is trusted and does not require authentication and authorization. In contrast, zero trust architecture assumes that everything is untrusted and requires strict authentication and authorization measures to limit access to sensitive data and critical systems.
Is zero trust architecture only for large organizations?
No, zero trust architecture can be implemented by organizations of all sizes. The key is to define the scope of the project and develop a comprehensive security policy that addresses all aspects of the network.
Can zero trust architecture be implemented in a cloud environment?
Yes, zero trust architecture can be implemented in a cloud environment. In fact, it is recommended to implement zero trust architecture in a cloud environment to ensure the security of cloud-based applications and data.
How does zero trust architecture help with compliance?
Zero trust architecture helps with compliance by limiting access to sensitive data and critical systems. This helps organizations comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Is ZTA expensive to implement?
The cost of implementing zero trust architecture depends on the size and complexity of the network. However, the benefits of zero trust architecture far outweigh the costs in terms of improved security, reduced risk, increased agility, and enhanced visibility.
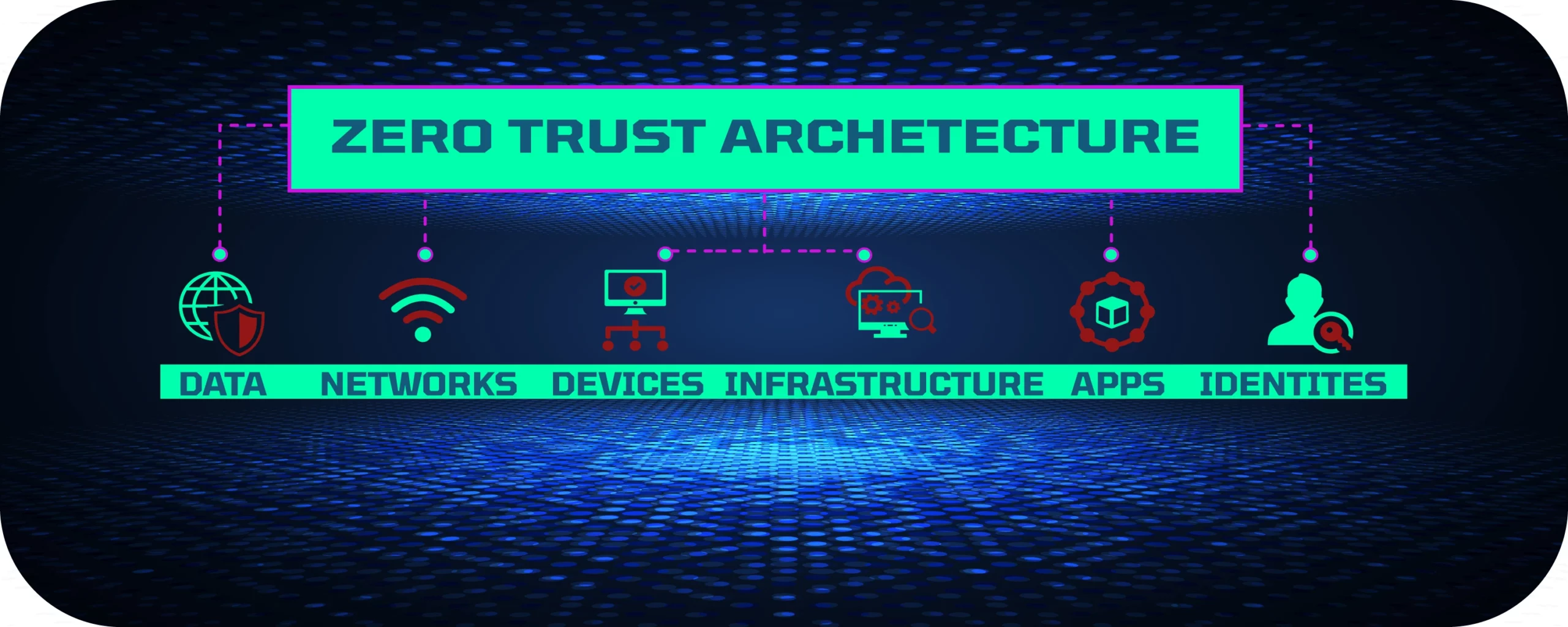
What are the core logical components of zero trust?
The core logical components of zero trust include:
- Authentication and Access Control: Authentication and access control are fundamental components of a zero trust architecture. Instead of relying solely on traditional perimeter-based security measures, zero trust emphasizes verifying the identity and authorization of every user and device attempting to access resources. This involves employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong authentication methods to ensure that only authorized entities can gain access. By implementing granular access controls, zero trust enables organizations to restrict privileges based on user roles, device characteristics, and other contextual factors.
- Network Segmentation: Network segmentation plays a crucial role in zero trust architecture by dividing the network into smaller segments or microperimeters. This approach aims to minimize the potential impact of a security breach by containing threats within isolated network zones. By segmenting the network, organizations can control and monitor traffic flows more effectively, preventing lateral movement by attackers and limiting their ability to compromise other systems or sensitive data. Network segmentation can be achieved through technologies like virtual local area networks (VLANs), software-defined networking (SDN), and microsegmentation.
- Policy Enforcement: Policy enforcement refers to the implementation and enforcement of security policies across the entire zero trust architecture. Policies define the rules and criteria for granting or denying access to resources based on factors such as user identity, device health, and network context. With zero trust, policies are enforced at every access point, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can interact with specific resources or services. Policy enforcement mechanisms may include next-generation firewalls, secure web gateways, and identity and access management (IAM) systems.
- Visibility and Analytics: Visibility and analytics are critical components of a zero trust architecture, enabling organizations to gain insights into network activity, detect anomalies, and respond to security incidents effectively. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, such as network traffic, logs, and endpoint telemetry, organizations can identify potential threats and suspicious behaviors. Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques can help detect patterns, anomalies, and indicators of compromise in real-time, enabling proactive threat mitigation and continuous monitoring of the environment.
- Device and Application Inventory: Maintaining an accurate inventory of devices and applications is essential for implementing a zero trust architecture. Organizations need to have a comprehensive understanding of all devices connected to their network and the applications they are running. This inventory allows organizations to assess device health, identify vulnerabilities, and apply appropriate security controls. By maintaining an up-to-date inventory, organizations can enforce access policies based on device trustworthiness and ensure that only authorized and secure devices can access critical resources.
These core logical components work together to create a comprehensive zero trust architecture that focuses on continuous authentication, strict access controls, network segmentation, policy enforcement, visibility, and proactive security measures. By adopting these components, organizations can establish a robust security framework that helps prevent, detect, and mitigate potential threats in a dynamic and evolving threat landscape.
How Do I Choose a Zero Trust Provider?
When choosing a zero trust provider, consider factors such as their experience, expertise, and reputation. It is also essential to ensure that the provider’s solutions align with your organization’s needs and requirements. Additionally, consider the provider’s ability to offer ongoing support and maintenance for their solutions.
How Long Does It Take to Implement Zero Trust?
The time it takes to implement zero trust varies depending on the size and complexity of the network. A smaller organization with a less complex network may take a few weeks, while larger organizations with more complex networks may take several months to implement zero trust fully.
How and where does the solution deliver value, features, and risk reduction measures that go beyond the value of your existing security tools?
ZTA delivers value by providing enhanced security, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks, increasing agility, and providing enhanced visibility into network activity. Zero trust solutions offer additional features such as continuous monitoring, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control, which go beyond the capabilities of traditional security tools.
Is the zero trust scalable?
Yes, zero trust architecture is scalable and can be implemented in organizations of all sizes. The architecture can adapt to changing business needs and can be expanded or contracted as necessary.
What is Zero Trust Edge (ZTE)?
Zero Trust Edge (ZTE) is a security architecture that extends zero trust principles to the edge of the network, where devices and users connect to the internet. ZTE provides secure access to applications and resources for remote workers and branch offices.
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a security model that provides secure access to applications and resources, regardless of the user’s location. ZTNA uses identity-based access control and micro-segmentation to limit access to specific resources, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Conclusion
Zero trust architecture is a comprehensive security framework that provides enhanced protection against cyber threats. By limiting access to sensitive data and critical systems, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Implementing zero trust architecture requires a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of the network. By following the steps outlined in this article, organizations can enhance their security posture and protect their most valuable assets.
**Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice. Please consult with a qualified expert (such as us) for guidance specific to your organization’s needs.**